# Check Ingresses
The Entando Operator and custom resource controllers manage the ingresses which allow external access to services within an Entando cluster. The following directions show you how to examine these ingresses with two different methods.
# Using the OpenShift Dashboard
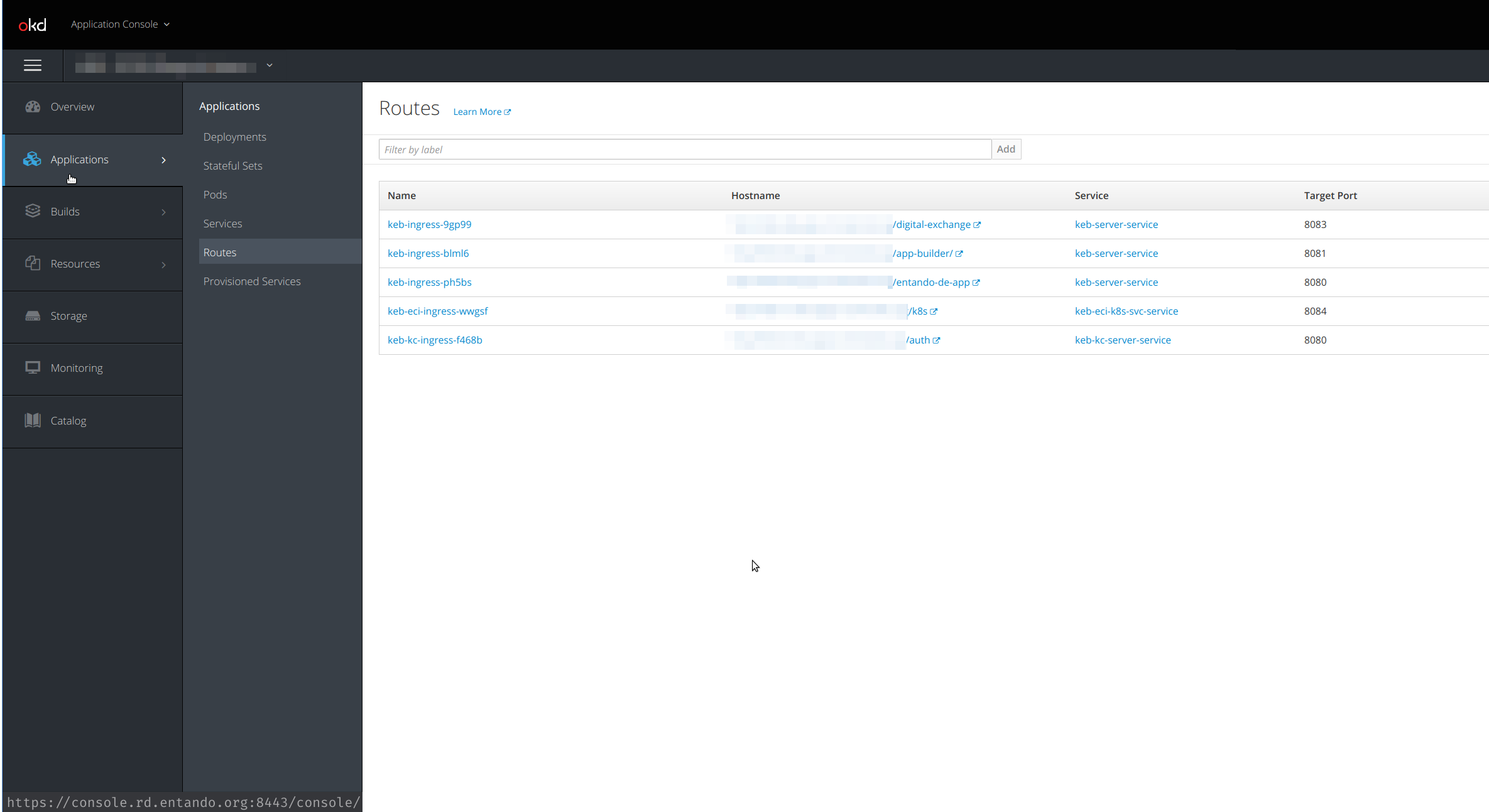
In the OpenShift dashboard, ingresses are not exposed directly as pods and deployments. The dashboard provides direct access to the ingress routes under the Applications → Routes menu.
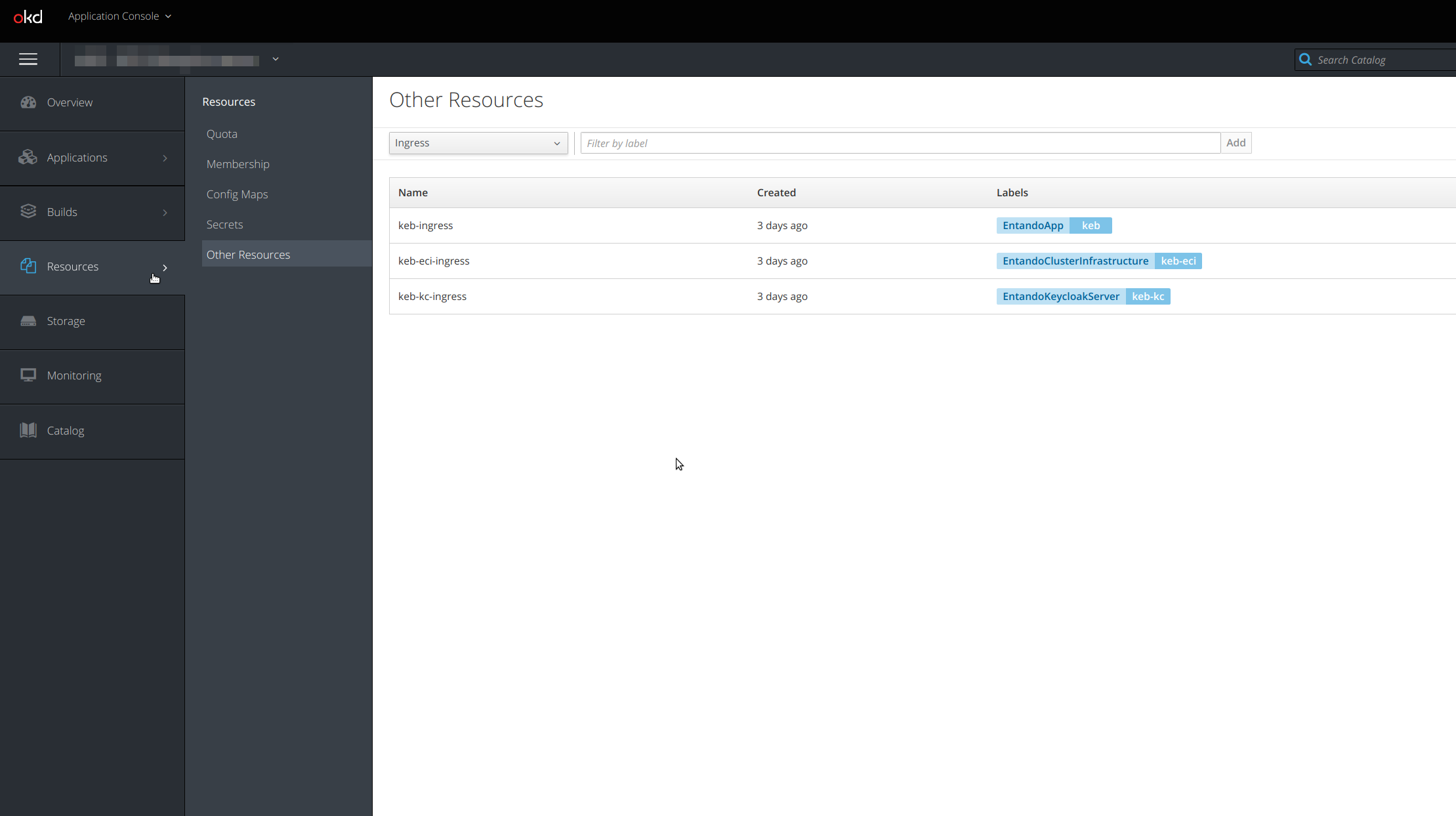
To see the ingress resources, choose Resources → Other resources from the left navigation menu. From the drop-down, select Ingress and you should see the ingresses available in that namespace or project.
# Using kubectl from the Command Line
- From the command line, use the following command with the namespace of your cluster:
kubectl get ingress -n YOUR-NAMESPACE
Here is an example of the result for the namespace entando:
> kubectl get ingress -n entando
NAME CLASS HOSTS ADDRESS PORTS AGE
default-sso-in-namespace-ingress nginx quickstart.192.168.64.15.nip.io 192.168.64.15 80 19d
quickstart-ingress nginx quickstart.192.168.64.15.nip.io 192.168.64.15 80 19d
- For more details about a specific ingress, use the kubectl
getcommand, specifying the ingress name you want to check and theyamloutput format.
> kubectl get ingress -n local quickstart-ingress -o yaml
apiVersion: extensions/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
creationTimestamp: "2020-05-13T15:27:08Z"
generation: 1
labels:
EntandoApp: qst
managedFields:
- apiVersion: extensions/v1beta1
fieldsType: FieldsV1
fieldsV1:
f:status:
f:loadBalancer:
f:ingress: {}
manager: nginx-ingress-controller
operation: Update
time: "2020-05-13T15:27:08Z"
name: qst-ingress
namespace: local
ownerReferences:
- apiVersion: entando.org/v1
blockOwnerDeletion: true
controller: true
kind: EntandoApp
name: qst
uid: aa7053e1-fd8b-419f-bdee-df3018c013fa
resourceVersion: "16802097"
selfLink: /apis/extensions/v1beta1/namespaces/local/ingresses/qst-ingress
uid: e9b6f027-369a-4b84-b4b1-736a6e49f180
spec:
rules:
- host: local.192.168.1.9.nip.io
http:
paths:
- backend:
serviceName: qst-server-service
servicePort: 8080
path: /entando-de-app
pathType: ImplementationSpecific
- backend:
serviceName: qst-server-service
servicePort: 8083
path: /digital-exchange
pathType: ImplementationSpecific
- backend:
serviceName: qst-server-service
servicePort: 8081
path: /app-builder/
pathType: ImplementationSpecific
status:
loadBalancer:
ingress:
- ip: 127.0.0.1
Learn More
- Learn more about Entando ingresses and architecture
- For more details about ingress concepts in Kubernetes, please refer to the Kubernetes Ingress documentation (opens new window).